Source: https://www.world-nuclear-news.org/Articles/Heysham-2%C2%A0to-address-issues-identified-after-IAEA
An International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) team's visit to the UK's Heysham 2 nuclear power plant "found areas of good practice" but also recommended improvements including in "setting and reinforcing expectations" for identifying and correcting "substandard conditions and equipment deficiencies in a timely manner".
The IAEA Operational Safety Review Team (OSART) mission took place in October 2023 at the request of the UK government. The missions - this was the 220th since 1982 - are designed to review operating practice in a wide range of areas across nuclear power plants.
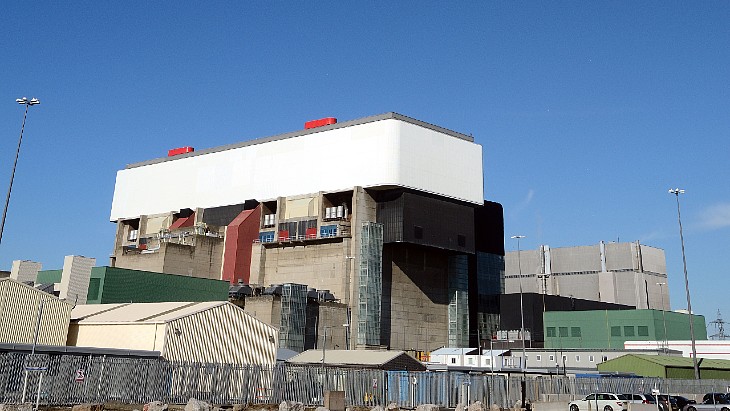
In this case the 13-strong OSART team included experts from Brazil, Canada, Finland, France, Germany, Slovakia, Sweden, the USA, and three IAEA staff members, with the team having 354 years of collective nuclear power experience. Heysham 2, in Lancashire on the northwest coast of England, features two 620 MWe advanced gas-cooled reactors which began operation in 1988 and are due to end operations in 2028.
Areas of good practice highlighted in their newly published report includes the implementation of a "wall hound" system to "detect electromagnetic interference and radio frequency interference (EMI/RFI, including Bluetooth) emitted by mobile phones, laptops and smart watches raising an audible and visual cue/prompt". Also the use of hot connection indicators to monitor cable connections temperatures and "the use of chemistry preservation metric by the plant to monitor system status". The use of military training expertise for staff is also praised, especially as it relates to stressful or emergency situations.
The wall hound system was installed in 2020 at three key locations: "the entrance to the RCA, the reactor building, and in the safety circuit/main control room. Certain devices are authorised for use by the plant staff and provisions are established to determine whether detected items are allowed or prohibited".
Initially it detected about 450 devices a month, but that number is now down to about 300 devices per month, of which about five are unauthorised and require action to be taken. The report adds: "The benefit of the Wall Hound System is the prompt detection of EMI/RFI which could impact sensitive plant equipment and possibly impair equipment function resulting in a transient or plant trip."
The most significant proposals for improving operational safety were:
- The plant should improve its approach in setting and reinforcing expectations and challenge the site personnel to identify and correct substandard conditions and equipment deficiencies in a timely manner.
- The plant should improve the material conditions of some plant systems, structures, and components to further reduce the risk to plant safety and reliability.
- The plant should improve the control of fire doors and storage in the plant to further reduce fire risk to equipment and personnel safety.
As an example of the first of those areas the report says "during the review the team observed the following, field operators were not systematically identifying and reporting all deficiencies, additional equipment/materials were left at work sites, without proper fire loading risk assessments, the need for a number of maintenance tasks to be reworked, material deficiencies open for long time periods due to large work backlogs, oil leaks on all diesel generators, unsecured items in seismically controlled areas, contamination and occupational exposure control shortfalls".
The OSART team's 82-page report noted challenges caused by staff turnover but praised the safety culture at the plant, saying: "The team identified that the plant has a good reporting culture enabled by a respectful work environment. The operating experience is well embedded and communicated: morning briefs involve all plant personnel and are customised if needed, the use of event briefs in pre-job briefs is relevant. In addition, the decision-making is rigorous and a conservative approach has been clearly demonstrated."
It also said that "Heysham 2 NPP management expressed their commitment to address the issues identified and invited a follow up visit in about eighteen months to review the progress".
Operator EDF said the report "noted nine areas of good practice ... which can be replicated globally, and provided eight recommendations for further improvement". Heysham 2 Station Director Martin Cheetham said: "The nuclear industry is always working to drive forward improvement, which is why regular in-depth reviews involving international experts are important. They supplement our own internal processes and our work with our regulator, the Office for Nuclear Regulation.
"Safety is our overriding priority and we greatly value the recommendations provided to the station. We have also invited the IAEA back to review our progress."
The Department for Energy Security and Net Zero said the OSART mission reviewed 10 areas: Leadership and Management for Safety; Training and Qualification; Operations; Maintenance; Technical Support; Operating Experience Feedback; Radiation Protection; Chemistry; Emergency Preparedness & Response; Accident Management.
It added that "during the mission, the international experts observed that safety performance at Heysham 2 was good" and the department "welcomes the report from the IAEA and looks forward to a follow-up mission conducted by the IAEA in around two years' time. We would also like to thank and commend EDF Energy and Heysham 2's leadership and plant personnel for hosting the mission, for their positive engagement with the review team and their commitment to nuclear safety. The UK Government is confident that good progress will be made by EDF Energy on the further enhancements suggested by the IAEA and recognises the positive feedback provided by IAEA on the operational safety of Heysham 2".
In his foreword to the report, IAEA Director General Rafael Mariano Grossi stressed that an OSART mission "is not a regulatory inspection to determine compliance with national safety requirements ... each review starts with the expectation that the plant meets the safety requirements of the country concerned. An OSART mission attempts neither to evaluate the overall safety of the plant nor to rank its safety performance against that of other plants reviewed. The review represents a 'snapshot in time'; at any time after the completion of the mission care must be exercised when considering the conclusions drawn since programmes at nuclear power plants are constantly evolving and being enhanced."
In 2016, the second unit at Heysham 2 set a world record for uninterrupted operation of a commercial nuclear power reactor, following a 940-day run.