Source: https://www.world-nuclear-news.org/Articles/UK-completes-transfer-of-Winfrith-waste-drums
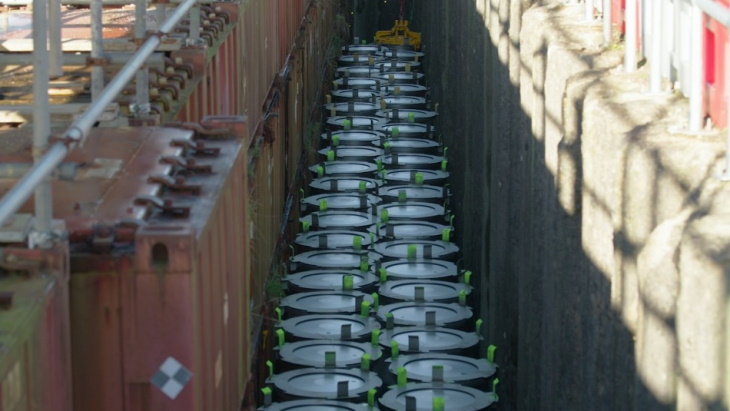
A project to transfer more than 1000 drums of radioactive waste from the Winfrith site in Dorset, in southern England, to the Low Level Waste Repository site in Cumbria, in northwest England, has been completed earlier than expected.
The project was an accumulation of eight years' work and has seen 11 consignments of drums transported by rail from Winfrith to the LLW Repository site.
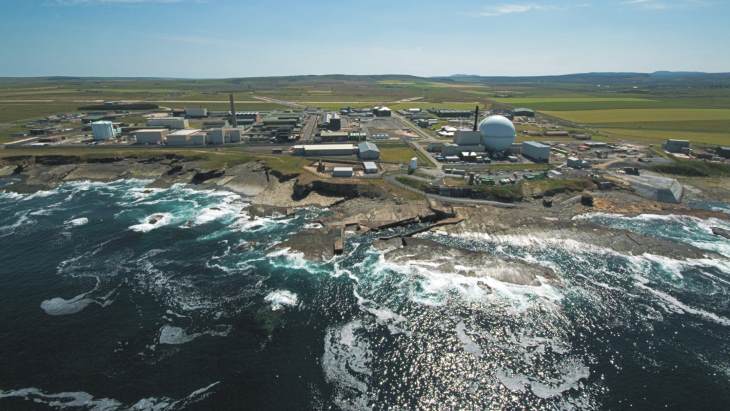
A total of 1068 drums of waste from the Winfrith Steam Generating Heavy Water Reactor (SGHWR) - which ceased operations in 1990 - were placed in the Treated Radwaste Store at the Dorset site, awaiting transfer to the intermediate-level waste storage facility at the Harwell site in Oxfordshire. However, the period of radioactive decay means the drums are now classed as low-level, rather than intermediate-level, waste, allowing early disposal at the LLW Repository, the UK's primary LLW disposal facility.
The drums have been disposed of utilising void space in Vault 8, optimising the use of the LLW Repository, and freeing up the Winfrith facility for alternative use or decommissioning, the UK's Nuclear Decommissioning Authority (NDA) said. Final disposal of this waste has also removed the requirement for long-term storage, saving money for the UK taxpayer.
The initiative was a collaboration with Nuclear Waste Services (NWS), Nuclear Restoration Services (NRS) and Nuclear Transport Solutions (NTS), which are all part of the NDA group.
"The retrieval operation of the drums from the store went really well," said Laura Street, NRS's head of waste at Winfrith and Harwell. "We managed to improve our timings on each retrieval, meaning that the final drum was retrieved well ahead of schedule. The shipment of the drums by rail provided significant savings to the taxpayer and also saved 7502 kg of carbon emissions for each rail shipment compared to transporting these drums by road.
"This achievement takes us another step closer to completing our decommissioning mission and returning the site to heathland with public access."
Howard Falconer, Head of Waste Services at NWS, added: "Seeing the final train arrive at the LLW Repository was a proud moment and significant milestone for this successful project. It is the result of years of collaborative planning and preparation by Nuclear Waste Services, Nuclear Restoration Services, Nuclear Transport Solutions and our extensive supply chain partners involved.
"Planning and preparation were key to the success of this project with NWS staff working with Winfrith Site to explore alternatives to manage the waste more effectively. This work is integral to our mission, to make the UK’s nuclear waste permanently safe, sooner."
SGHWR was a 100 MWe prototype reactor which operated from 1968 until 1990, supplying electricity to the grid as well as performing its prime function of supporting research into water-cooled reactor technology. It is one of only two remaining reactors - both of which are being decommissioned - at Winfrith. The 84-hectare site was a centre for nuclear research and development to enable vital research into reactor design and was home to nine experimental reactors at various times from the 1950s to the 1990s.