British government is seeking to attract outside investors to the £20 billion project.
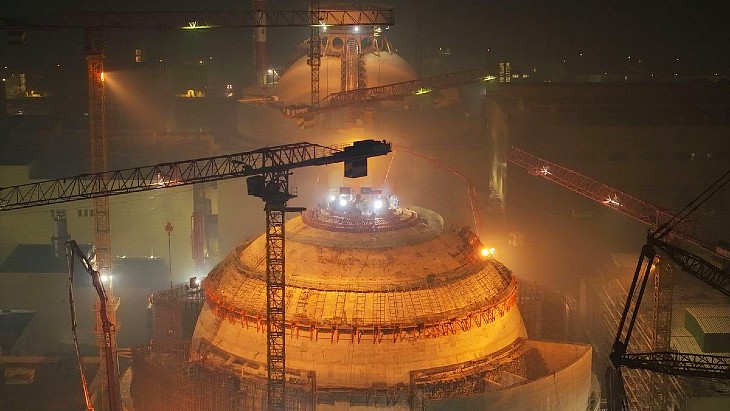
The British government has injected an extra £1.3bn (€1.5bn, $1.6bn) to support the construction of two France-supplied EPR nuclear plants at Sizewell C in southeast England.
The funding is the largest to date and will allow early construction works at the £20bn facility to continue ahead of a final investment decision later this year.
The money comes from existing budgets will support continuing preparatory work such as improvements to roads and rail lines around the Suffolk site, ensuring the necessary local infrastructure is in place before full construction begins, a government statement said.
It said committing further government support at this stage will help the project stay on schedule and keep down overall costs.
Andrew Bowie, minister for nuclear, said the latest funding “sends a strong message to investors that Britain is serious about its low-carbon, homegrown nuclear-powered future”.
The additional funding for the planned nuclear station comes as ministers seek to attract outside investors to the project.
It means the government has now committed £2.5bn to pave the way for the proposed Sizewell C, up from £1.7bn previously.
Sizewell C is being developed by EDF, France’s state-owned utility, and a final investment decision is due later this year.
Formal Green Light For Construction
A development consent order (DCO) triggered by Sizewell C on 15 January gave the formal green light for construction to begin and released £250m funding for initiatives for the local community and environment. A DCO is an application for consent to undertake a “nationally significant infrastructure project – major infrastructure developments that include power plants.
Investing an additional £1.3bn consolidates the government’s position as the majority shareholder in the project, reached in December 2023. It follows a £700m funding pledge in November 2022 and a further £511m agreed last summer.
Earlier this month the government announced the biggest expansion of nuclear power for 70 years, with a nuclear roadmap setting out how the UK will quadruple nuclear power generation to up to 24 GW by 2050, up from about 5.8 GW today.
The roadmap commits to exploring another GW-scale power plant similar in scale to Sizewell C, simplifying regulation and building a fleet of small modular reactors.
It could potentially lead to the construction of about 11 new large-scale reactors by 2050 – enough to meet a quarter of the national electricity demand.
Approval will be given for one or two new reactors every five years from 2030 to 2044, and backing given to another large-scale nuclear station in addition to Hinkley Point C – a project which has seen delays and rising costs – and the planned Sizewell C, each of which will have two France-supplied EPR units.
Background: Falling Output, No New Plants
The share of nuclear energy in the UK’s electricity generation has fallen to around 15% from 27% in the 1990s as older plants have been decommissioned and no new plants have come online.
The output of the UK’s fleet of nine units was 37.3 TWh last year, 15% lower than the year before because of station closures and statutory outages.
Since 2000, the UK has seen permanent reactor shutdowns at Bradwell, Calder Hall, Hinkley Point A, Hinkley Point B, Hunterston, Oldbury, Sizewell, Chapelcross, Dungeness and Wylfa. The last unit to go offline was Hinkley Point B-1 in August 2022.
The government and developer EDF started a process last year to bring private equity investment into the planned Sizewell C project, with EDF saying a sustainable commercial model is needed for a final investment decision.
EDF Energy, the UK-based subsidiary of EDF, said recently it is planning to extend the life of four nuclear power stations in the UK and invest £1.3bn in its nuclear fleet as it aims to maintain UK nuclear output at current levels until at least 2026.
The French energy company said it would make a decision on whether to extend the life of the four advanced gas-cooled reactor stations – Torness, Heysham A and B, and Hartlepool A – by the end of the year. This would require regulatory approval.
EDF Energy operates all of Britain’s five nuclear power stations that generate electricity. A further three are defuelling (Hunterston B, Hinkley Point B and Dungeness B), the first stage of decommissioning.