Source: https://www.world-nuclear-news.org/Articles/Hungary-aims-to-extend-life-of-Paks-nuclear-plant
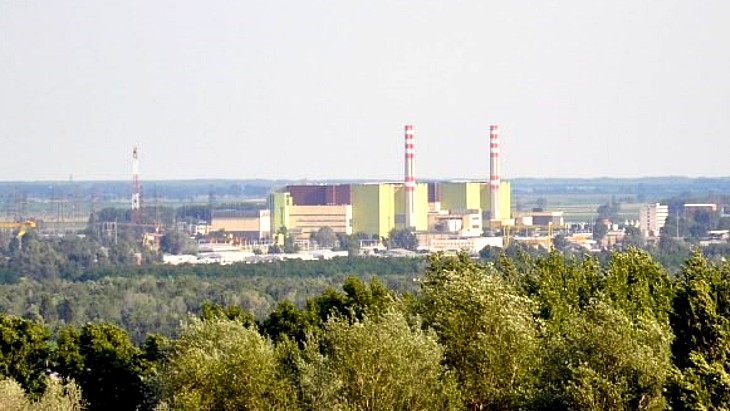
The operator of the Paks nuclear power plant in Hungary has notified the European Union of the country's intention to extend the operating lifetime of the four units to 70 years.
Péter János Horváth, CEO of operator MVM Paksi Atomerömű Zrt, said that in accordance with Euratom regulations the announcement of the extension plan had been made to the EU and "this marks the beginning of the roughly decade-long process" to extend the operating licence by another 20 years.
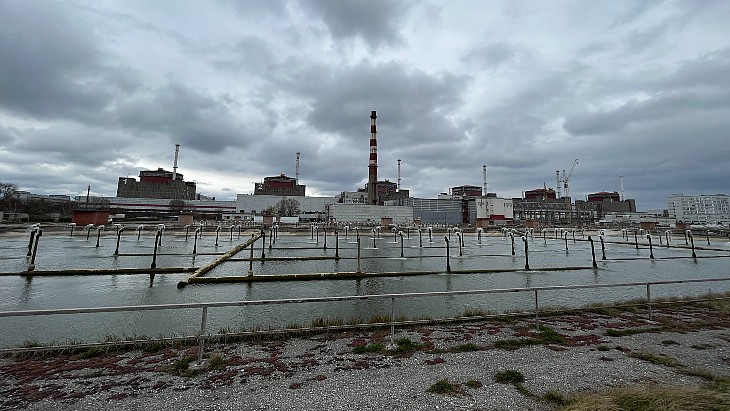
The existing four units at Paks are VVER-440 reactors that started up between 1982 and 1987 and they produce about half of the country's electricity. Their design lifetime was for 30 years but that was extended in 2005 by 20 years, to between 2032 and 2037.
Horváth said: "This power plant is no longer the same as the one that started operating four decades ago: thanks to continuous developments, renovations, safety-enhancing measures - and not least the responsible, dedicated team of professionals with extraordinary knowledge and experience - this power plant today is already a generation more advanced than it was when it started.
"At the same time, during the process of extending the operating hours, we examine and evaluate each bit of our equipment and systems and, if necessary, replace them, all of course in accordance with international practice, under strict official control, as we have always done. As a result of the operation and maintenance practices developed with maximum commitment to safety and a responsible, good stewardship approach, the Paks nuclear power plant is fully capable of serving Hungary for decades to come."
The company says that the plant has an important role to play in Hungary's energy security as well as helping combat climate change, preventing the release of about 250 million tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions since it began operating. At a press conference to announce the life extension programme, it was also stressed that as a state-owned company "we consider it a strategic issue to further extend" the operating life of the plant.
The company said that from 2024 it would be holding three year's worth of nuclear fuel at the site. The increase from the two years held previously is intended to "to reduce the uncertainties resulting from the conflict in Ukraine".
According to the official About Hungary, Deputy Director Pál Tóth said the extension would require the completion of some 250 reconstruction projects, and is reported to have said on potential costs that "revamping the electric and control systems would be in the EUR1.5 billion range (USD1.6 billion)". The full implementation plan is expected to be submitted in 2028.
Hungary's existing nuclear reactors at Paks produce about half of its electricity. In addition to the lifetime extension project there is also a project - Paks II - to build new nuclear capacity. It was launched in early 2014 by an intergovernmental agreement between Hungary and Russia for two VVER-1200 reactors to be supplied by Rosatom, with the contract supported by a Russian state loan to finance the majority of the project. The construction licence application was submitted in July 2020 to construct Paks II alongside the existing Paks plant, 100 kilometres southwest of Budapest on the banks of the Danube river. The construction licence was issued in August 2022 with groundworks having started this year and a construction schedule agreed last month.
Safely extending the operating lifetime of existing nuclear power plants was one of the points made by governments and industry in their COP28 pledges to support the tripling of nuclear energy capacity by 2050.