this post was submitted on 06 Dec 2024
110 points (99.1% liked)
askchapo
22816 readers
248 users here now
Ask Hexbear is the place to ask and answer ~~thought-provoking~~ questions.
Rules:
-
Posts must ask a question.
-
If the question asked is serious, answer seriously.
-
Questions where you want to learn more about socialism are allowed, but questions in bad faith are not.
-
Try [email protected] if you're having questions about regarding moderation, site policy, the site itself, development, volunteering or the mod team.
founded 4 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments

Absolutely. Climate change is already causing earthquakes and it always has. Land that was located underneath continental glaciation during the Last Glacial Maximum is still rising rapidly every year in a process called isostatic rebound, and this can result in earthquakes. This will, of course, increase as more glaciers melt. The most worrisome result from this is not necessarily the size of the earthquakes, but any corresponding landslides caused by rebound or earthquakes that could result in tsunamis.
Additionally, extraction of groundwater or oil can result in earthquakes as the water is removed and ground must subside. The same applies to oil extraction through traditional wells and fracking. We’ve actually created entire new seismic zones just by extracting the resources we then use to create climate change.
Also, and probably mostly important in the longer term than will majorly impact us, we can expect to see increased volcanic and earthquake activity along the edges of many tectonic plates, as the weight from water that used to be sequestered in glaciers over thick, continental crust is redistributed over thin, oceanic crust. The actual physical increase in weight (and thus pressure) can force water deeper into faults and also speed up subduction, thus resulting in increased earthquake frequency. We aren’t sure exactly how much of an impact this will have because it is extremely hard to measure.
Ah, word thank you for the info. Am I correct in thinking that stuff like changes in the ocean's currents and density (due to salinity) will also probably bring about pressure shifts on the sea floor? Like shifting your grip on a stress ball?
Not so much pressure on the seafloor that will matter, but changes in density are almost certainly going to impact currents and heat distribution. Winter in Europe is going to get very, very cold when the relatively warm Gulf Stream can not transfer its warmth to the air as effectively when it is stuck sitting underneath a 0.1°C layer of less dense fresh water that just melted from glaciers in Greenland, which is already measurably happening. It’s pretty much the only place on the planet seeing an average drop in sea surface temperature for that reason.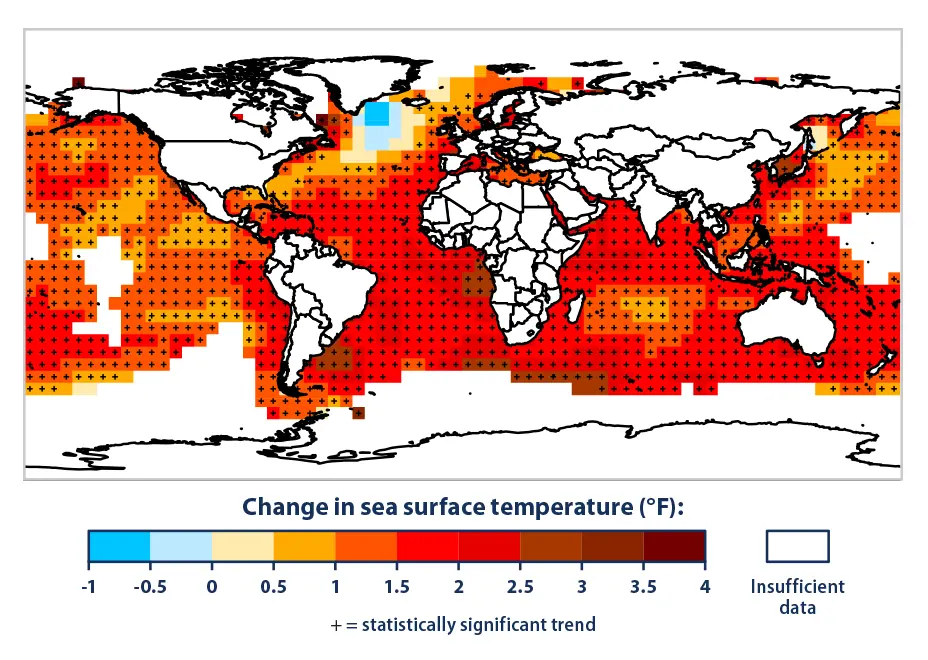
Just as melted ice appears to be flowing south off Greenland, am I looking at a warming effect here caused by the outlets of the Plata, the Kongo, and the Tumen?
If so, why specifically those?
It’s quite possible that’s the reason, and we do know that inland waters in rivers and streams are also increasing in temperature. At least in the cases of the Rio de la Plata and Congo, it certainly appears to be the case. As for the Temur, I think there isn’t as easy an argument to be made, as it drains into a pretty isolated section of sea that would naturally be prone to heating more easily. The Congo looks like the strongest case, especially because it has no estuary. That being said, I’m not going to commit to an answer because I don’t have the data myself.