Apologies for posting.
I should say by way of introductory remarks, that while this is an effort post, it is an effort post on a shitposting website, and thus ab initio a shitpost and therefore be taken in the correct spirit of levity in which it is intended. Don't get my thread locked.
Recent discussion on here has touched on the moral status of the execution of the Romanov family by Bolsheviks ahead of the advancing White Army^1^. While not exactly of practical significance given how few of us have Royal Families locked up in our basement, it did reveal several significant, (sometimes severe) differences in the philosophical underpinnings of the posters on this website.
A Moral Communism
Moral status as such actually has very little to deal with communism/leftist (in the Marxian vein) in terms of it's internal mechanism. Marx, Engels, Lenin, and the rest of that intellectual lineage^2.^ famously thought very little of moral philosophy. A communist is thus entirely at liberty to dismiss this entire discussion as idealism, and observe that within a Marxist framework, there are no 'good' and 'bad', merely a historically deterministic sequence of class antagonisms that will eventually resolve in favor of the proletariat and thus choosing to be a communist is merely choosing to throw one's hat in with the predetermined victors. This strand of amoral communism thus is not terribly interested in this discussion, and anyone here that adheres to that framework is excused from the discussion as having won the argument.
Given the rest of us do have moral considerations that prefigure our political beliefs, it's necessary for us to sketch out at least a scaffolding for what moral commonalities leftists share before going further, lest we fall into a morass of fundamentally incompatible frameworks stemming from different axiomatic premises. Speaking from my own personal position, I ascribe to leftist political positions as they offer me the greatest promise of granting a comfortable and dignified existence to the largest number of people possible. That in of itself does not make a moral axiom though, as achieving a large amount of something is valueless if the individual components don't themselves have value, and therefore, and a fundamental value informing my politics is the axiomatic value/sanctity of human life. So I am taking on as an assumption that generally speaking, want everyone to have dignified and comfortable lives^3.^ If that position doesn't more or less describe you, you are also excused as having won the argument.
Justifying Shooting a Tsesarevich in my Pajamas
Which brings us to the Romanovs. In keeping with ^3.^ above, and considering the minor children of royals not culpable for the systematic injustices perpetrated under the dictatorship of their parents, we'll limit our discussion here to the minors (Anastasia, and especially Alexei), though I think the general outline of the argument can be applied to pretty much all of the Tsar's issue. The entirety of the family, along with their retinue, were bulleted and bayoneted in Yekaterinburg about 10 days before white occupied the city. In attempting to defend the legacy of one of the most politically successful socialist projects in history^4.^, this action has largely been justified on the left. Examining the commonly proposed justifications in light of our moral principles finds them universally lacking.
- It was necessary in order to safeguard the immediate success of the revolution against an individual with claim to the throne.
This argument goes that while we do value human life and dignity, our efforts to maximize these will sometimes require that certain human lives be forfeit, essentially turning this into a trolley problem^5.^. This argument differs in an important aspect from the trolley problem in that the trolley problem consists of single moment in time with clearly articulable and certain outcomes given at the outset. Leaving Alexei alive was in no way certain to doom the revolution to failure of significant struggle, as he could have been maintained in custody, and ascribing such outsized influence on the course of political affairs to the life of a sickly 13 year old is a profoundly anti-materialist approach to history. History is replete with challenges to establish socialist authority^6.^, none of which stemmed from claimants to the Imperial thrown. Further, liquidating the Tsar, his children, and his brother did not exhaust the Romanov line, his cousin could and did proclaim himself Emperor-in-exile, and despite being old enough to actually head a restorationist intervention, none materialized. So the notion that killing Alexei was necessary fails to stand up to scrutiny ^7.^. It is also worth noting as an aside that the Romanovs were deeply unpopular, and to wit, were not the government the Bolshevik revolution occurred under, and supporters of the provisional government (domestic and international alike) formed the overwhelming contingent of the White forces, and the notion that a 14 year old tsarist claimant to the thrown would have had a meaningful impact on that colossal clusterfuck strains credulity.
- It prevented a longterm challenge to Boshevik control in a manner similar to Jacobite uprisings or the Bourbon Restoration.
Taking a more longterm view of the problem, it might be acknowledged that the Alexei presented no immediate threat justifying his liquidation, but, drawing from the history of pre-CIA regime changes, he presented a longterm likely/probable/plausible/possible threat in the form of an eventual challenge, and that acting in light of that possibility was justified if not strictly necessary. If we wish to examine this in light of our moral principles, we need to develop some notion of probability calculus; at what point is taking in innocent life now justified in order to avoid certain possible harms that have a certain probability of occurring. You can formalize this to ridiculous extents^8.^, or you can take the legal systems more qualitative approach, of establish some standard of proof (you are, after all, justifying killing someone), where the execution is deemed justified if seems more likely than not/clearly and convincingly/beyond a reasonable doubt that it will prevent further, greater harm in the future. This lets you weaken the requirement that it is necessary to kill him to merely it is prudent to kill him. What is lacking though is any evidence that anyone has meaningfully carried out this process for any standard beyond plausible. The greatest extent to which this is established is that historically, there have been several restorationist insurrections, but no systematized historical study has been undertaken to quantify the risk of insurrection/coup in the presence or absence of an legitimate claimant.^9^.
Well perhaps we leave it there; a plausible narrative that places Alexei as the cause of some harm is sufficient in our eyes to justify his liquidation. The problem with this is that it is such a liberal standard that it can be applied to nearly everyone. There are scores of documented peasant rebellions throughout history, so by the same standard it is plausible that any given peasant may be at risk for launching a peasant rebellion down the line and thus, by that same standard, we are justified in liquidating them. Universalizing from this generic peasant^.10. to all peasants. And thus our system named aimed an providing dignity and comfort is able to justify pretty much any atrocity.
- The moral culpability of for the executions lies at the feet of the Tsar who created the system and not the executioners themselves.
This argument goes that it was actually the Tsar that placed him in position to be killed by standing at the top of a monarchical system that has ruined and ended untold numbers of lives. Had the Tsar dismantled that system before it came to blows, Alexei would have lived a happily inbred life as a continental European curiosity.
This argument plays fast an lose with the notion of fault to an extent that borders on the absurd. Within getting into the morass that encompasses the legal notion of fault, I'll observe that the executioners where in total control of the situation, given the Romanovs were in the zone of immediate material influence, while the Bolshevik leaderships were at a more distant proximity, and Tsar Nicholas II at the head of the Imperial State was a fleeting memory, having greatly influenced the events that now overtook them, but having no control over them. The Bolshevik's in Ipatiev House or those in leadership in Moscow alone decided who in that house lived and died, they knew that, and they exercised that choice.
- Unpleasant things happen during a revolution and we accept that as soon as they begin.
This is true, but once again, it comes down to the notions of control and proximity. As a leftist, I acknowledge that the struggle for political power may involve the world becoming a worse place (as judged according to my moral principles outline above) due to my actions to make it a better one. This is an abstract acknowledgement. It may also result in me taking actions that I find unpleasant or repugnant^11^. If it is the moral principles that describe motivate my political struggle though, it is fundamentally self-defeating to exercise my control over my immediate surroundings to knowingly act in a manner that results in an immediate degradation of the world around me (once again, as judged by my moral standards). My actions in the here and now, must be justified according to my principles in the here and now and my actions in the here and now. If 10 minutes ago I was standing in Yekaterinburg and the Whites are closing in, and now I'm still standing in Yekaterinburg and the Whites are still closing in, but now there is a brand new pile of child corpses of my making, then I have made the world a worse place.
No tears for dead peasants
It is reasonable to ask why go to such great lengths to challenge the justifications for the murder of Alexei (which is so emotionally remote to me as to essentially be fictitious). To which I offer the following justifications.
- It's ridiculous and therefore funny.
- Because eventually some of us may be in positions to make decisions that make the world a substantially better or worse place for others, and I want it be very clear what stands before us when making those decisions. No, none of us are going to decide whether or not an heir lives or dies, but we are going to decide how to treat with those around us, and want everyone to pause before they exercise what little control they have in the world around them before making it a worse place, justifying it with a glib aphorism or some half-baked argument.
^1.^ The fitness for humor here is not considered, as something can be both morally bad and the legitimate target of well-done comedy. Like 9/11.
^2.^ I was promised ice cream if I didn't say 'ilk' here.
^3.^ To wit, one of the main justifications for political violence on the left is that it is directed at those preventing others from enjoying dignity, comfort, or well, life.
^4.^ Such as it is.
^5.^ which we may dub the Yekaterinburg Streetcar Defense
^6.^ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Rebellions_in_the_Soviet_Union
^7.^ One could alternatively take the logical form of necessity as a conditional, ~P -> ~Q with P being "the legitimate claimant to the imperial thrown is killed" and "Q" being "the revolution is successful". Given the contra-factual nature of ~P, the truth value of this statement can't be evaluated directly, but given the analogous situation in China with PuYi, we can strongly infer that this conditional is in fact false and thus logical necessity is not present.
^8.^ define x~i~ to be each enumerated possible future in space X, p(x~i~) to be the probability of that future occurring, and h(x~i~) to be the number of lives ruined by Alexei in that future x~i~. Shoot kid if
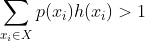
^9.^ To reach a preponderance of evidence standard you would need to establish P(Insurrection|Legitimate Claimant) > P(Insurrection), which the strictly materialist interpretation would hold P(Insurrection|Legitimate Claimant) = P(Insurrection).
^10^ Regular viewers will recognize this as universal generalization.
^11^ Orwell's description of the conditions of fighting in the Spanish civil war come to mind.
You are plainly conflating sociological morality with actual morality. Yes, the idea of morality and the social construction of moral sensibilities have a massive impact on society, but that does not mean there is any objective "good" or "bad" that influences the material world (and therefore would itself be physical).
I'm going to jump in here because I've been thinking about this for a while - morality does exist that is neither arbitrary nor transhistorical, there is an objective morality that arises for each particular class, from the specific historical material conditions of that particular class.
The proper morality of a class can be derived objectively from what is both necessary for them to sanction as moral actions to maintain their system, and what is necessary for them to believe about themselves and their system, at a given point in history. So, Feudal morality values loyalty and deference to your lord through the lens of Christian loyalty to god in order to keep the feudal structure stable, Bourgeoise morality values the supposed superior hard work and abilities of the capitalists "born equal" to the workers to justify their superior position - this is obviously just the superstructure rising from the base, but is a part of the superstructure that cannot be called anything but morality and yet clearly exists on an objective, non-arbitrary basis (these beliefs aren't held just because members of that class subjectively decided to choose them).
The difference is that we as proletarians, using dialectical materialism - the philosophical system proper to our class - can consciously understand the reason behind our intuitively arising morals (rather than having to write a mythologized "Genealogy", for instance). It becomes apparent to a conscious worker that it is objectively good for our class for feminism, antiracism, LGBTQ acceptance etc. to be implemented; but even without consciously understanding it, the mechanics of class struggle and the necessity of solidarity with fellow workers for your own rational self-interest naturally lead workers to feminist, anti-racist and LGBT-accepting conclusions* - unless that process is disrupted by intentional bourgeoise interference, of course. This is important because it means that as proletarians we can truthfully claim - to our undecided fellow proletarians - that we are not amoral, that we in fact have a definite, non-arbitrary, superior morality to the capitalists, and opposition to those morals are objectively bourgeoise intrusions. As a concrete class, we DO have objective goods, as defined for us by our concrete historical conditions.
(* and after the revolution, the mechanics of a centrally organised worker-run economy require these things for maximum efficiency!)
You're essentially talking about class consciousness or class interest, depending on the specific framing, with occasional deviations into ideology that is downstream of these things (in the bourgeois example in particular)
I guess this is just a "these gentlemen think that by changing the names of things, they have changed the things themselves", but if morals are a set of consistent principles about what is good and bad, and a proper understanding of class gives you a set of consistent principles about what is good and bad for your class, why not call it morality? EVERY other moral code is actually the same thing anyway.
Detractors say communism is amoral, implying we have no principles at all. Marxism itself makes no moral arguments sure, it's a purely scientific description of social development, but it can describe the origin of previous superstructures' systems of morality, and also describe what set of behaviors proletarians would intuitively (or organically or whatever) construct a moral system around. It's just that we can also consciously, rationally find out those things for ourselves as a class UNLIKE feudalists or pre-Marxist capitalists.
I suppose having thought more about it, I should reframe this as a tactical decision for convincing people who are concerned with 'morality', because by their standards we actually do have morals, and we can define what those are and why we have them. And it also means we can definitively say that patsocs or social chauvinists or anti-trans vulgar materialists who call themselves socialist or whoever, do not represent a rigorously applied scientific socialism. I guess I'm saying that, having eliminated the category of "transhistorical, universal truths of good and evil for guiding human behaviour", there nevertheless is a real category of social objects in the superstructure called 'moral codes', and we as communists do kind of have one AND it arises on an objective basis AND we can and should bludgeon reactionaries with it.
A prescriptive, conditional statement is not the same as morality except by playing word games. I am not doing a moral good* by, I don't know, pre-heating the oven at the correct temperature according to the recipe I am following, I am simply doing what is necessary to follow the recipe. When I kill a mosquito, it is not because leaving it alive would be evil, but because leaving it alive would produce a set of circumstances that I would prefer less. You might as well say that someone who is "good" at making ice sculptures is doing moral good by making those ice sculptures, it is just an equivocation because English has a blind spot here.
*don't do some Peter Singer bullshit here, you know what I mean
Okay yes, as a class conscious proletarian EVERY action is essentially that. The recipe for constructing a maximally efficient economy includes the instruction "be antiracist", so being antiracist is 'merely' an operationally correct behaviour to produce a preferred result. But in unconscious people, clinging to some subjectively cobbled together set of moral truths halfway between capitalist ideology and their own lived experience, that statement won't spark anything whereas "real communists MUST consider being antiracist to be morally good" will AND it's functionally true, it's just like... the silhouette of a more advanced understanding.
"Communists are amoral" is ground we have no reason to cede, when for some we can explain that universal morality doesn't exist but here are the rational scientific reasons for our positions, and for others we can say actually here is a set of principles communists are obliged to hold JUST LIKE any other moral code.
I apologise to mr cascade if i misinterpreted his argument. But the point seems to be that sociological morality is objective but not absolute because each is a reflection of specifc material conditions.
And if there is a common logical relationship between the set of sociological moralities and the set of material conditions. That would be a way to descrive an objective morality.
Thus whats moral is whats in the interests of your class. Wich seems like the middle ground betwen platos and trasymarchuses view
Its not necessarily class conciousnes but rather you are able to act more morally as you gain class conciousnes.
Because when people talk about morality, especially in a philosophical context, they are talking about "if there is a significant truth to moral claims and what that truth is." e.g. Is the statement "Murder is immoral" meaningfully true or false? That is also what it means when one says Marxism is amoral, it refuses the idea that statements like the preceding have truth values.
What you are talking about are personal values, not anything like that. No one is denying that people have their own moral sensibilities and that they act on those sensibilities besides certain freaks at the fringes of academia ("radical behaviorism," if you are interested).
You are just talking about ideology